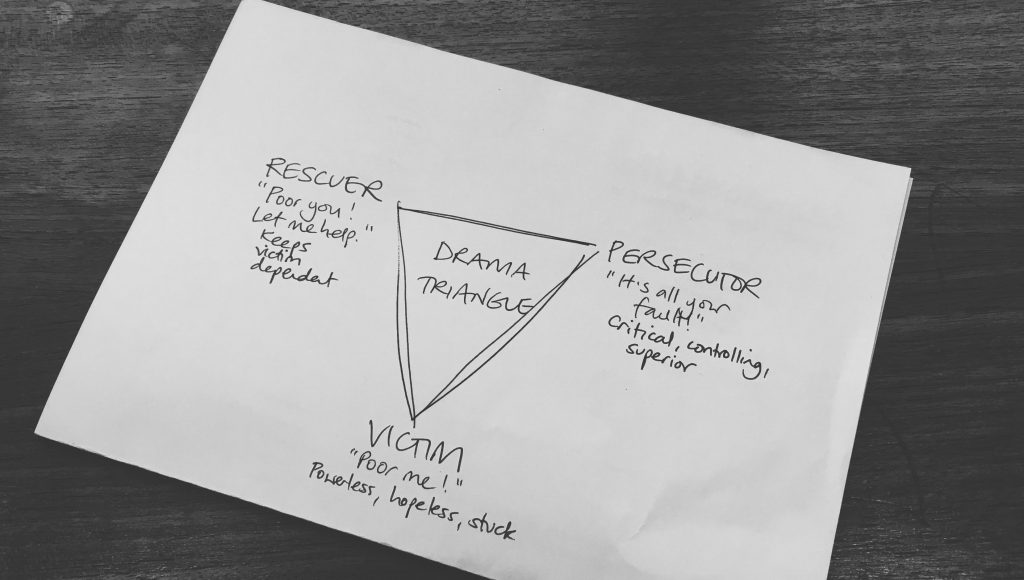
What is Focusing?
Focusing was developed in the 1960s by Eugene Gendlin when he was researching why some people were able to sustain a more lasting change from psychotherapy than others. He found that those who made more sustained changes had a natural ability to check within themselves for an inner felt sense of a situation or difficulty, and to use that felt sense to intuitively find a way forward. Gendlin developed a process in order that those people who don’t have this natural ability, could be taught to develop it.
Focusing is…………
- A tool for supporting self-compassion
- A self-help exercise
- A way of life
Focusing is all of these – and more.

My own experience is of a history of getting stuck in my head, trying to think my way out of an uncomfortable situation or experience – believing that if only I could figure out the right solution, I’d stop feeling so distressed / uncomfortable / anxious. This resulted in lots of overthinking, rumination and self-criticism for not being able to get it right. Focusing has helped me develop another, much gentler way of managing difficult thoughts and feelings, which means that even when I get triggered back into old patterns of overthinking, I’m better able to recognise what’s happening and to move through it more quickly.
For me it’s been nothing short of life-changing, which is why I decided to complete the training to teach other people this wonderful skill.
How Focusing can help
Many of us learn at an early age to suppress feelings, or to be frightened of strong emotions. This can be a result of experiences of feeling unsafe in childhood, may have been modelled to us by our parents, or may have been part of the conditioning of the society or culture we grew up in – there are lots of possible reasons. Over time this can lead to us being afraid of our feelings – you might be afraid that if you let yourself feel, you’ll be overwhelmed by your emotions, like opening Pandora’s Box. In some cases we become so skilled at not allowing our feelings that we’re not even sure what we feel.
Even if they’re buried deep, those feelings don’t go away, and can often manifest themselves in other ways, including physical symptoms, poor immune response, anxiety, stress symptoms, or erratic moods.
Focusing with a skilled companion, you can learn to acknowledge, first of all, that there is something there that wants attention. You can begin to listen to what those suppressed parts of you want to say – while keeping a safe distance. Doing this with a supportive teacher helps you be alongside thoughts or feelings, rather than be overwhelmed by them. You can recognise that the feelings are part of you – they’re not all of you. With practice, you can learn to build relationships with those inner parts of you, and the intense feelings will ease as those denied voices realise that, actually, they don’t need to shout so loud to be heard.

How does Focusing compare to mindfulness or meditation?
There are similarities between all three practices. They all aim to bring the attention inside the body, and to remain in the experience of the present moment.
However, often with meditation and mindfulness, the intention is to not get ‘caught up’ in thoughts or feelings, but to let them pass. With Focusing we bring interested curiosity to a thought, feeling or sensation. We might enquire what it’s like, what it might be connected to, and we want to stay with it in a friendly way. With this curiosity more can arise and stuck feelings can shift.
Is Focusing a type of guided visualisation exercise?
Some people will have a lot of visual imagery when they’re Focusing, but some people will have body sensations, or thoughts, or memories (and lots of people have a mixture). In my own process, I often find I start with a body feeling and then images can also come later. My role is to support people to allow images or other experiences to arise, and to find ways of describing the experience. In that process, where these ‘parts’ are attended to by trying to describe ‘just what they’re like’, images may develop into other images, or emotions, or memories.
When someone is new to Focusing, I’ll make suggestions, like ‘perhaps you could sense if there’s an emotional quality to this image’, or ‘if it feels helpful, perhaps you could check if there’s something this part is wanting’, to support a dialogue or relationship with these inner experiences. As people become more experienced with Focusing, they’ll often learn what’s helpful for them, e.g. whether they like having suggestions or .

Should I choose Focusing or counselling?
Focusing is not therapy, although it does, of course, have therapeutic benefits. If you come to me for Focusing sessions, you’ll be learning a self-help practice, which you can also do on your own, and if you decide to take it further, you could develop Focusing partnerships with other people who are learning Focusing. The role of the teacher or companion in Focusing is to support you (sometimes via suggestions) to follow your own direction. You don’t need to give me any history, unless you want to, as we will be dealing with your present-moment experience in sessions, even though this experience will most often be influenced by past events.
Because Focusing has become an integral part of who I am, it is also an element of my counselling process. For example, I may suggest a pause within a session, to check inside, to allow some space for feelings to emerge. I sometimes also offer some Focusing teaching within counselling sessions, if I think that it may be helpful to tune in to some feeling or experience that seems difficult to put into words.
If you have a clear goal of what you want to change in your life or behaviour, it may be that counselling is more appropriate than Focusing. If you’re not sure what you want, it could be that Focusing might help you get a clearer idea of your steps forward. If you want to develop a better relationship with yourself, Focusing and counselling could both help with this.
I suggest that, if you want to try Focusing, we plan in 3 sessions initially. My reason for this is that, for some people, it can seem a bizarre and unusual way of relating to themselves, and the unfamiliar can be uncomfortable. Committing to a few sessions means that you give yourself a better chance of moving through this discomfort, where something in you might be tempted to shy away after the initial experience. Also, we’ll take some time during the first session, for some preparation before the guided exercise, and some feedback afterwards, whereas a greater proportion of the second and third sessions can be dedicated to the experience of you being with yourself.
What happens in a Focusing session?
I’ll ask you to close your eyes (or look down if you prefer), and then lead you into your body with a body-scan or check-in, then use gentle suggestions to see what’s there wanting your attention, or to check in with a particular issue that you want to look at.
You describe to me what you experience and I reflect that back to you. I may make suggestions to help you to begin gently to build a relationship with what comes up. We’re not attempting to analyse or interpret – although part of you may want to, in which case I’ll encourage you to acknowledge that aspect of you, too.

I’ll give you a time signal that we’re coming to the end, and I’ll suggest you take some time to thank whatever has shown up, then encourage you to come back to the room and open your eyes.
If you want you can talk about what happened in the session, and you can ask for my feedback if you think that would feel helpful.
What is Focusing most useful for?
Anxiety
I’ve found Focusing particularly helpful with clients who have high levels of anxiety, who often feel compelled to keep busy at all times and/or to focus their energies on trying to keep others happy. Anxiety can provoke over-thinking, ruminating thoughts, and compulsive behaviours as a way of filling up any empty space which might otherwise be occupied by strong feelings. With Focusing we can turn towards those feelings that are provoked if you don’t keep busy, and you’ll discover that anxiety is something that you don’t need to react to or ignore. When you acknowledge the anxiety, and turn a compassionate and curious attitude to what may be underlying it, the intensity of the feelings will lessen and become easier to tolerate.
Trauma
Focusing can be a wonderful way of soothing the parts of you that are easily triggered due to past traumatic experiences – without having to go into the story of the trauma. This means it can be equally useful if you experience triggering or fight/flight/freeze reactions, even if you don’t think you’ve been subject to traumatic events. Because of the Focusing principle of being alongside your experience – as an observer, or witness – rather than being in it, you can get a little bit of distance from your emotions. We work with your in-the-moment, embodied present, and having the experience of being able to be in relationship with your traumatised parts can be profoundly healing at a whole-body level.
Inner critic
Focusing treats the critical voice as a part of you – not all of you. By using Focusing to build a relationship, you can develop understanding of how that inner critic has your best interests at heart – even if it doesn’t feel like it. The inner critic tends to develop as a protective device (based on some kind of childhood belief that if it works you hard enough you’ll be loved / you won’t be abandoned), and by your responding to it with compassion, it will learn over time that it doesn’t need to push you as hard.

Pre-therapy sessions
As mentioned above, Gendlin developed the Focusing process to support people to get more out of their therapy. I believe that developing your skills of listening to all parts of you, can be helpful as a precursor to counselling sessions – whether with me or another therapist.
Focusing for therapists
Focusing is a great resource for counsellors and therapists to help them manage their own thoughts and feelings stimulated during sessions with clients. Some counsellors find it difficult, sometimes, to engage with their own personal therapy, because a sense of competition or fear of being judged by their therapist can hamper their ability to be honest during sessions. The emphasis in Focusing is on developing the client’s relationship with themselves, more so than their relationship with the Focusing teacher. I don’t need to know any history or events and I don’t need to know what a particular feeling, memory etc, is connected to, in order to support your process, which means that Focusing may be experienced as a safer space than counselling at times. In addition, because I don’t need to know about the content, I can offer Focusing to people that I have existing relationships with, in a way that I would never do with counselling.
I find it hard to describe exactly what Focusing is, in a way that really conveys its essence! The best way to really understand it is to try it for yourself. If it sounds like something you’d be interested in – please get in touch with me.
Further reading and resources
What is Focusing? – The International Focusing Institute
What is Focusing? – the British Focusing Association
Eugene Gendlin talks about Focusing
Get a feel for Focusing via this video: